Characterization of Quality Attributes and Analysis of Influencing Factors in HIGH SHEAR MIXER GRANULATION
Characterization of Quality Attributes and Analysis of Influencing Factors in HIGH SHEAR MIXER GRANULATION
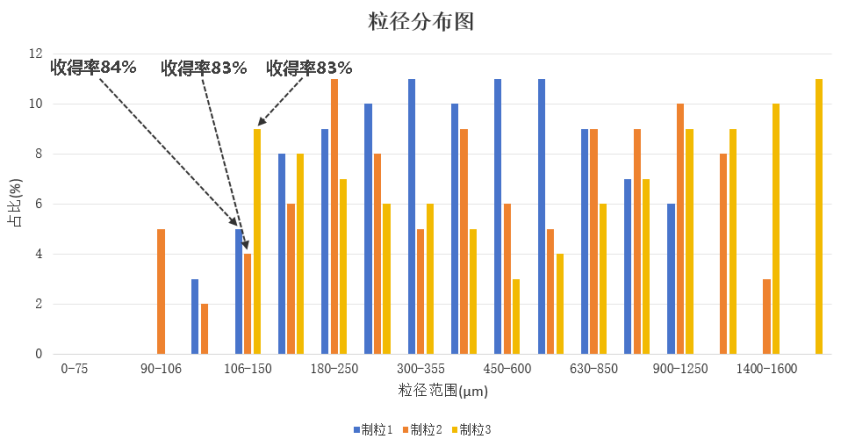
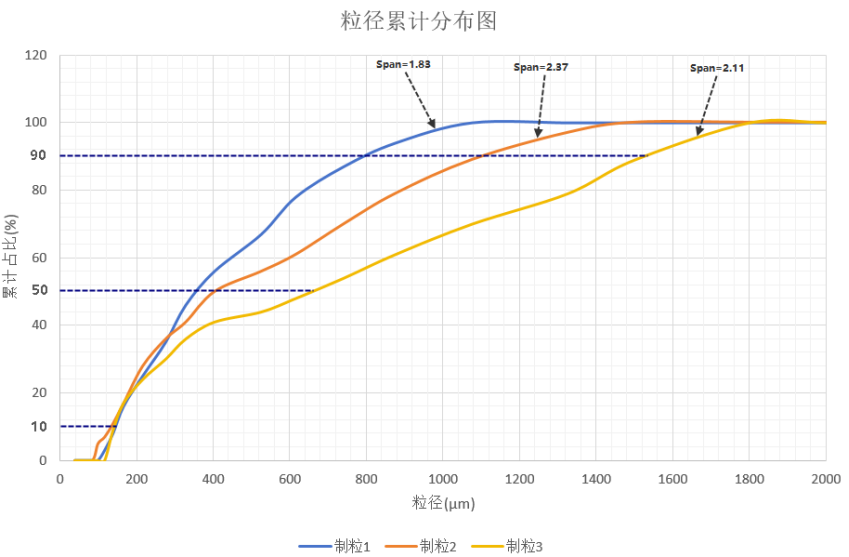
The High Shear Mixer Granulation technology is widely used in the field of solid pharmaceutical preparations. This technology usually mixes raw materials and excipients evenly to form particles of 180-2000 μ m, which are used in downstream processes such as tablet pressing, capsule filling, and particle bagging. The implementation of wet granulation process is crucial for supplying high-quality and qualified particles downstream. The properties of particles affect the key quality attributes of products, such as dissolution rate, differences in tablet weight (differences in loading volume), and so on. Usually, we can evaluate particles based on physical indicators such as particle size distribution, porosity, moisture content, and flowability. The target particle size yield refers to the percentage of particles that meet the expected particle size range in the final product to the total particle mass, which can be measured by screening, laser, and image methods. According to the industry standard JB/T 20015, the performance evaluation standard for wet mixing granulators is that the particle rate of corn starch, dextrin, and sugar powder in a 3:2:1 ratio after drying should not be less than 75% within the range of 180-2000 μ m. Enterprises confirm the particle size of wet granulation based on downstream process requirements, and the particle size range and particle rate are subject to specific product requirements. The particle size distribution describes the proportion of particles of different sizes in a particle system, while the dispersion degree is quantified by the width of the particle size distribution. The particle size distribution is obtained through statistical methods based on the results of particle size detection. Even if the target particle size yield is the same, there may still be significant differences in particle size dispersion. For most drugs, we prefer a smaller particle size dispersion within the expected yield range of the target particle size to ensure consistency in the medicinal dissolution effect. The particle size distribution width Span is commonly used to measure the degree of dispersion of particle size distribution. The calculation method is as follows: (1) In the equation: D90- the particle diameter corresponding to the cumulative count of particle size from small to large reaching 90% of the total, μm; D10- the particle diameter corresponding to the cumulative count of particle size from small to large reaching 10% of the total, μm; D50- the particle diameter corresponding to the cumulative count of particle size from small to large reaching 50% of the total, μm。 The larger the span, the greater the difference in particle size and the poorer the uniformity; Conversely, the more uniform it is. Figure 1 shows the difference in particle size distribution width of particles prepared using the same raw materials and different process parameters. It can be seen that although the target particle size yield of 180-2000 μ m is similar, the difference in particle size distribution width is significant (the blue curve has a smaller Span value, the yellow curve has a moderate Span value, and the orange curve has a larger Span value). Therefore, selecting the appropriate Span value based on process requirements is an important focus in evaluating the effectiveness of wet granulation.